Understanding Sustainable Living: Definition & Examples for a Greener Future

Table of Contents
In an era where environmental concerns are at the forefront of global discussions, the concept of sustainable living has gained immense significance. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), sustainable living involves adopting practices that reduce our environmental footprint, promote ecological balance, and contribute to the overall well-being of the planet. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the definition of sustainable living and explore practical examples that showcase its implementation. Let’s embark on a journey to understand how we can make conscious choices for a sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
What is Sustainable Living?

Sustainable living is a lifestyle that aims to minimize the impact of human activities on the environment by making choices that are ecologically responsible and economically viable. This approach emphasizes reducing waste, conserving resources, and fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and the natural world.
Defining Sustainable Living
At its core, sustainable living is about meeting our present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves a holistic perspective that considers environmental, social, and economic factors. The key principles of sustainable living include the following:
- Environmental Responsibility: Adopting practices that minimize environmental degradation and promote conservation.
- Social Equity: Ensuring that the benefits and burdens of sustainable practices are distributed fairly among all communities.
- Economic Viability: implementing practices that are economically feasible in the long run, avoiding depletion of resources.
Incorporating Sustainable Living Practices into Daily Life
To truly understand sustainable living, let’s explore practical examples that highlight its application in various aspects of our daily lives.
Sustainable Living at Home: A Comprehensive Guide

Sustainable living at home is a cornerstone of adopting an eco-friendly lifestyle. This section explores practical tips, examples, and advice for individuals looking to make their homes more sustainable.
Energy Efficiency: Lighting and Appliances
- Switch to LED Bulbs: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED bulbs. LED lights not only consume less energy but also last longer, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Unplug Devices: Even when turned off, electronic devices consume energy in standby mode. Unplug chargers, electronics, and appliances when not in use to eliminate this “phantom” energy usage.
- Invest in Energy Star Appliances: When purchasing new appliances, look for the Energy Star label. These appliances are designed to meet strict energy efficiency guidelines, reducing both energy consumption and utility bills.
Sustainable Home Design: Green Building Materials
- Use Recycled or Upcycled Materials: Incorporate recycled or upcycled materials into home renovations. This includes reclaimed wood, recycled metal, or repurposed materials, reducing the demand for new resources. The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) provides valuable insights into green building practices.
- Consider Modular Design: Modular construction allows for energy-efficient and sustainable building practices. Prefabricated modules are constructed off-site, minimizing waste and reducing the environmental impact of construction.
- Optimize Natural Light: Maximize the use of natural light to reduce reliance on artificial lighting. Consider large windows, skylights, and light-colored interior finishes to reflect and amplify natural light.
Waste Reduction and Recycling: A Zero-Waste Approach
- Practice the Three Rs: Embrace the mantra of Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. Reduce your overall consumption, reuse items whenever possible, and recycle materials like paper, glass, and plastic.
- Composting: Set up a composting system for kitchen scraps and organic waste. Composting not only reduces landfill waste but also creates nutrient-rich soil for gardening.
- DIY and Upcycling Projects: Engage in do-it-yourself (DIY) projects and upcycling to give new life to old items. Transform discarded furniture, clothing, or household items into something functional and aesthetically pleasing.
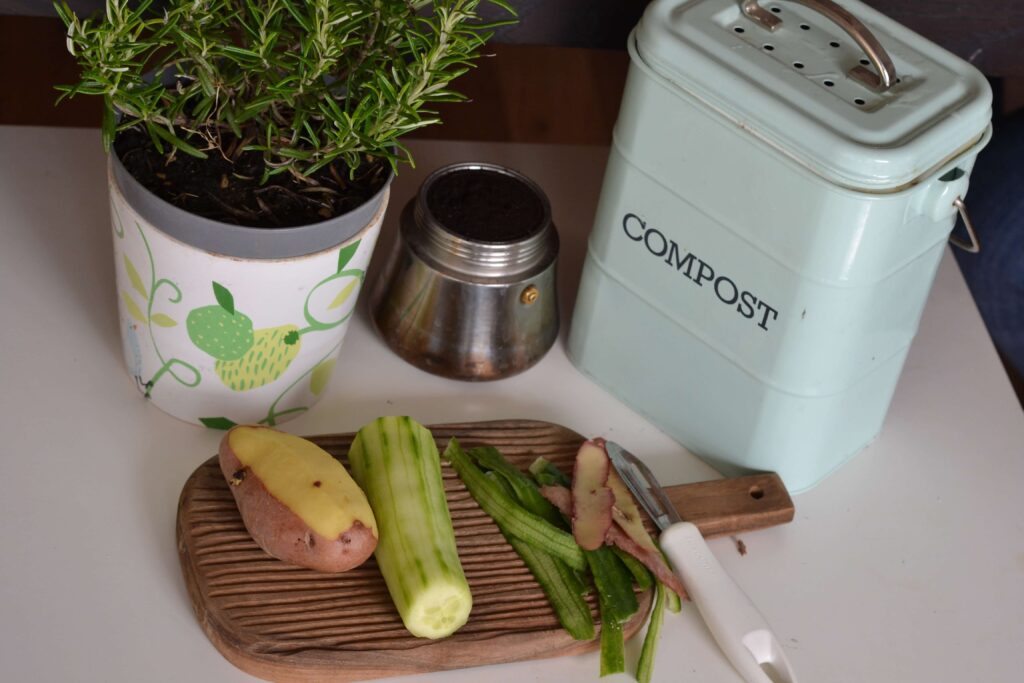

Water Conservation: Practical Tips
- Fix Leaks Promptly: Address any leaks in faucets, toilets, or pipes promptly. A dripping faucet may seem minor, but it can waste a significant amount of water over time.
- Install Low-Flow Fixtures: Upgrade to low-flow faucets, showerheads, and toilets to reduce water consumption without sacrificing performance.
- Collect Rainwater: Consider installing a rain barrel to collect rainwater for watering plants. This reduces reliance on treated tap water for outdoor irrigation.
Tips for Beginners: Taking the First Steps
- Conduct a Home Energy Audit: Identify areas of energy waste in your home by conducting a home energy audit. Many utility companies offer this service or provide resources for a DIY audit.
- Start Small: Begin with small, manageable changes before tackling more significant initiatives. This could include switching to reusable shopping bags, reducing single-use plastics, or incorporating meatless meals into your diet.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about sustainable living practices and innovations. Read books, attend workshops, and explore online resources to deepen your understanding of eco-friendly living.
Sustainable Living Beyond the Basics: Advanced Tips
- Install Solar Panels: For those ready to make a more substantial investment, consider installing solar panels on your property. Solar energy not only reduces your reliance on the grid but can also lead to long-term cost savings.
- Embrace Smart Home Technology: Incorporate smart home technology to optimize energy usage. This may include smart thermostats, energy-monitoring devices, and automated systems that adjust settings based on occupancy.
- Create a Sustainable Garden: Grow your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs using sustainable gardening practices. This includes organic gardening, companion planting, and minimizing the use of synthetic pesticides.
Sustainable Transportation: Navigating the Eco-Friendly Way
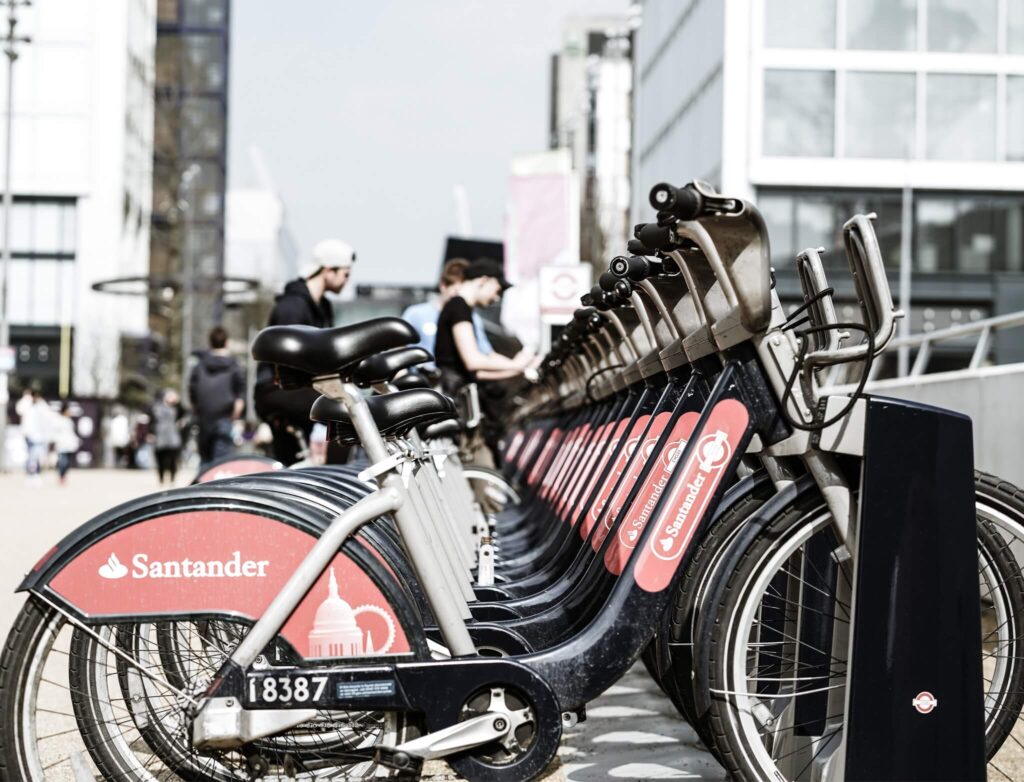

Green Commuting: Beyond Fossil Fuels
- Cycling and Walking: Choose sustainable modes of transportation like cycling and walking for short distances.
- Public Transport: Utilize public transportation to reduce individual carbon footprints.
- Electric Vehicles and Carpooling: Consider electric vehicles and carpooling to further minimize the environmental impact.
Sustainable Urban Planning: Creating Green Communities
- Walkability: Prioritize walkable neighborhoods with easy access to amenities.
- Green Spaces: Advocate for and support the creation of green spaces within urban environments.
- Efficient Public Transportation: Promote and utilize efficient public transportation systems for sustainable city living.
Sustainable Food Choices: Nourishing the Body and the Planet
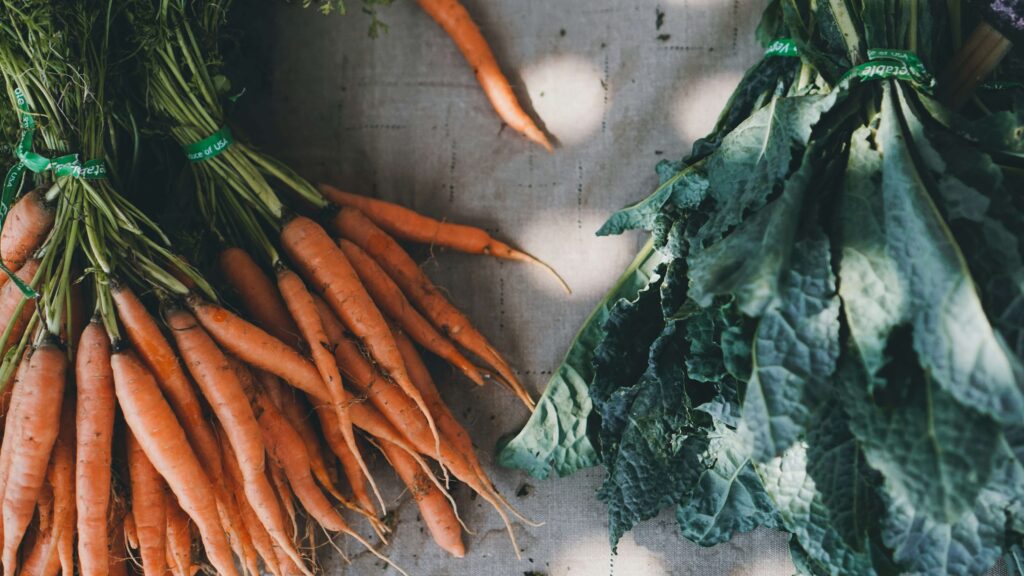

Plant-Based Diet: Reducing the Carbon Footprint
- Embrace a Plant-Based Diet: Reduce meat consumption to lower greenhouse gas emissions and support animal welfare.
- Local and Seasonal Eating: Support local farmers and choose seasonal produce to reduce the carbon footprint of food transportation. To reduce our carbon footprint, initiatives like the EAT-Lancet Commission provide valuable insights into sustainable diets, and platforms like Local Harvest help connect consumers with local, sustainable food sources.
Sustainable Fashion: Redefining Style with a Conscience

Ethical and Eco-Friendly Clothing
The fashion industry is a major contributor to environmental degradation. Sustainable living in this context involves opting for ethical and eco-friendly clothing options, such as those made from organic or recycled materials. In the realm of sustainable fashion, organizations like Fashion Revolution advocate for ethical practices, while platforms like Good On You offer ratings for ethical and sustainable fashion brands.
Minimalism and Slow Fashion
Embracing minimalism and adopting a “slow fashion” approach characterized by high-quality, timeless pieces contributes to reducing the environmental impact of fast fashion.
Overcoming Challenges and Looking to the Future

Economic Barriers: Paving the Way for Affordability
- Government Incentives: Advocate for and take advantage of government incentives and subsidies for sustainable practices.
- Community Initiatives: Participate in community initiatives that promote sustainability and offer support.
Cultural and Behavioral Shifts: Transforming Mindsets
- Education and Awareness: Promote education and awareness campaigns to foster cultural and behavioral shifts toward sustainable living.
- Inclusivity: Ensure that sustainable living practices are inclusive and accessible to diverse communities.
The Future of Sustainable Living: Innovations and Collaborations
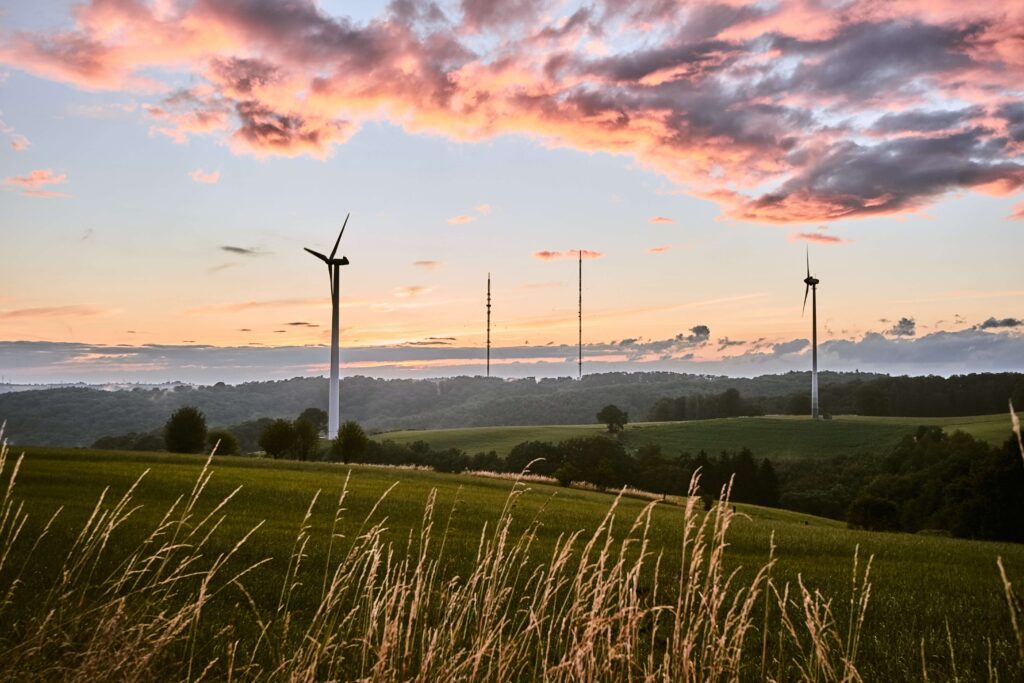

Technological Integration: Shaping Tomorrow
- Renewable Energy Technologies: Embrace advancements in renewable energy technologies such as solar and wind power.
- Smart and Sustainable Cities: Support the development of smart cities with efficient infrastructure and sustainable practices.
Global Collaboration: United for a Sustainable Future
- International Agreements: Advocate for and participate in international agreements and collaborations for global environmental sustainability.
- Shared Commitments: Encourage shared commitments to address global environmental challenges.
In conclusion, sustainable living is not a distant ideal but a tangible and necessary way of life. By incorporating these sustainable practices into our daily lives, we contribute to a healthier planet for current and future generations. From eco-friendly homes to sustainable transportation, conscious food choices, and ethical fashion, each decision shapes the world we live in. Let us collectively embrace the principles of sustainable living and pave the way for a future where environmental responsibility is a shared commitment. Together, we can forge a sustainable legacy that transcends individual actions, creating a positive impact on the planet we call home.